This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>![]()
This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>![]()
Enterprise products, solutions & services
We have been in the 5th-Generation of Fixed Network (F5G) era, where enhanced fixed broadband (eFBB), guaranteed reliable experience (GRE), and full-fiber connection (FFC) are provided to support fiber to the home (FTTH), fiber to the room (FTTR), and fiber to the office (FTTO), and fiber to the machine (FTTM) applications for multiple industries and broadband users.
Going forward, we are entering the F5G-advanced era, where we will further improve eFBB and FFC by providing 10 times higher bandwidth and 10 times more connections, as well as enhancing GRE by providing level-4 autonomous driving network (ADN).
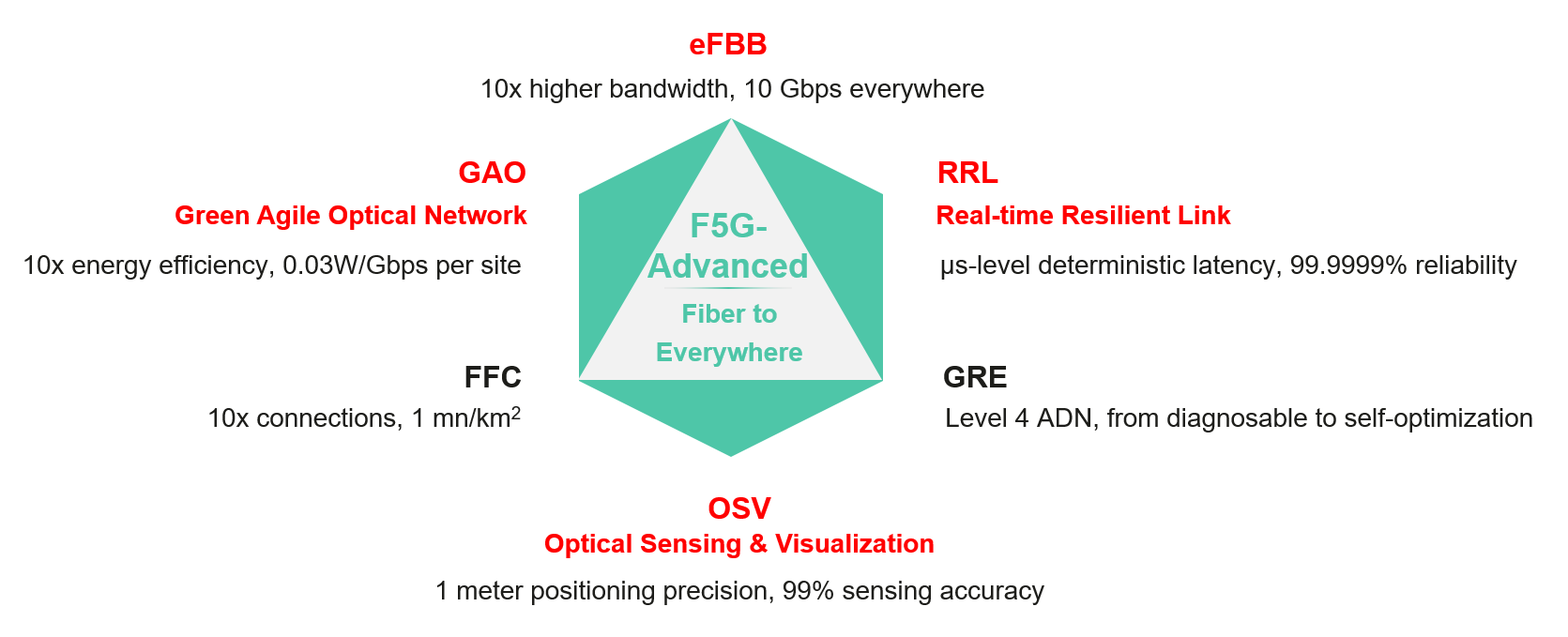
Now with F5G-advanced, we have one important enhancement, which is real-time resilient link that provides microsecond-level deterministic latency and 6 nines of reliability (99.9999%). Here, we will be focusing on this new aspect for the contemporary power grid industry where we need very high reliability to support supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) networks for substations. One key aspect of this enhancement is the reduction of transport latency by using dense time division multiplexing (TDM) of timeslots that carry the communication services.
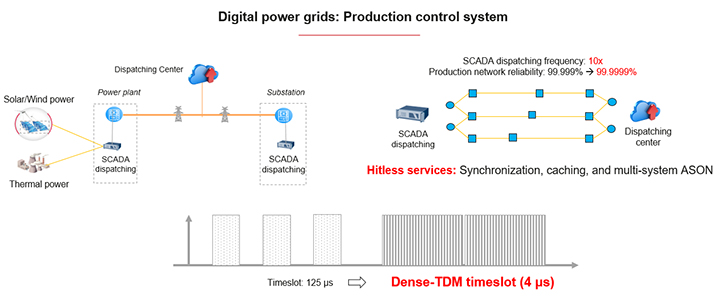
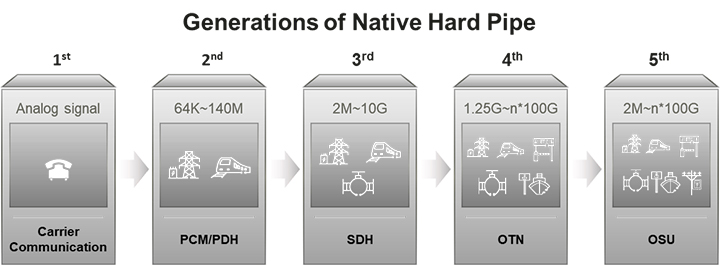
The key enabling technology is the optical service unit based optical transport network (OSU-OTN). This is a new native hard pipe (NHP) technology, which is regarded as the 5th-generation NHP technology that provides both high bandwidth and fine bandwidth granularity to enable smooth expansion of the transport capacity and the massive number of services connections to be supported. At the same time, high reliability and deterministic performance with nearly zero jitter and microsecond-level latency are realized.
With OSU-OTN, we can build a reliable all-optical base for industry digitalization by providing high service reliability, evolution scalability, and operation efficiency. A point-to-multipoint (P2MP) optical network architecture can be used to simultaneously support three different types of communication services with one single network, thereby achieving high efficiency. In addition, the coordination between the optical transport and access networks is enabling low-latency and high-reliability communication from end-to-end.
Firstly for service reliability, hard isolation guarantees the user experience and the quality of service being independent on other services in the same network. This is realized by the physical-layer isolation with dedicated TDM timeslots for any given services. Deterministic low latency is achieved with fine-granularity timeslots.
Secondly for evolution scalability, this new technology supports 100% smooth evolution because OSU-OTN's capability to scale bandwidth to multiple hundred Gbps per wavelength and multiple Tbps per fiber, yet with a very fine granularity of 2 Mbps to 10 Mbps, so that we can support a diverse set of applications with different bandwidth requirements with high reliability, low latency, and nearly zero jitter.
Finally for efficient operation, the three networks that are previously required to support the distribution communication network, the backhaul network, and the Internet of Things (IoT) network can be converged all together into with one single network by using the P2MP NHP architecture. Thus, one unified network can efficiently satisfy three different types of network requirements.
In terms of the advances in international standards, our industry is trying to develop a global standard on OSU-OTN, so that all the countries can benefit from this advanced technology. In an October 2018 ITU-T meeting in Geneva, people were already talking about the optical service unit based optical transport network. In February 2020, ITU-T Study Group 15 (SG15) established a work item named G.osu to standardize OSU-OTN. Later this month, there will be another SG15 meeting in the ITU-T headquarters in Geneva to further discuss about the G.osu technology designs. The aim of multiple global companies working on G.osu is to have global standards so that all the interested parties will benefit from OSU-OTN to realize efficient, reliable, and low-latency connectivity for all constant bit rate (CBR) and variable bit rate (VBR) services, as well as agile hitless bandwidth on demand.
With OSU-OTN, we will be witnessing a digital transformation to support contemporary power grid telecom networks with high reliability, scalability, and efficiency. Ultimately, global cooperation and collaboration among all interested parties are essential to realizing such digital transformation for a brighter future of the modern power grid industry.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy, position, products, and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. If you need to learn more about the products and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., please visit our website at e.huawei.com or contact us.